(For FYBCom Students & Future Accountants!)
Meet Rohan: The Café Owner ☕
Rohan spends money in two ways:
- One-Time Big Purchases:
- ₹5 Lakhs coffee machine
- ₹3 Lakhs furniture
→ Capital Expenditure
- Daily Running Costs:
- ₹10,000/month coffee beans
- ₹8,000/month electricity
→ Revenue Expenditure
Why care? Mixing these = Wrong profits, wrong taxes, exam mistakes!
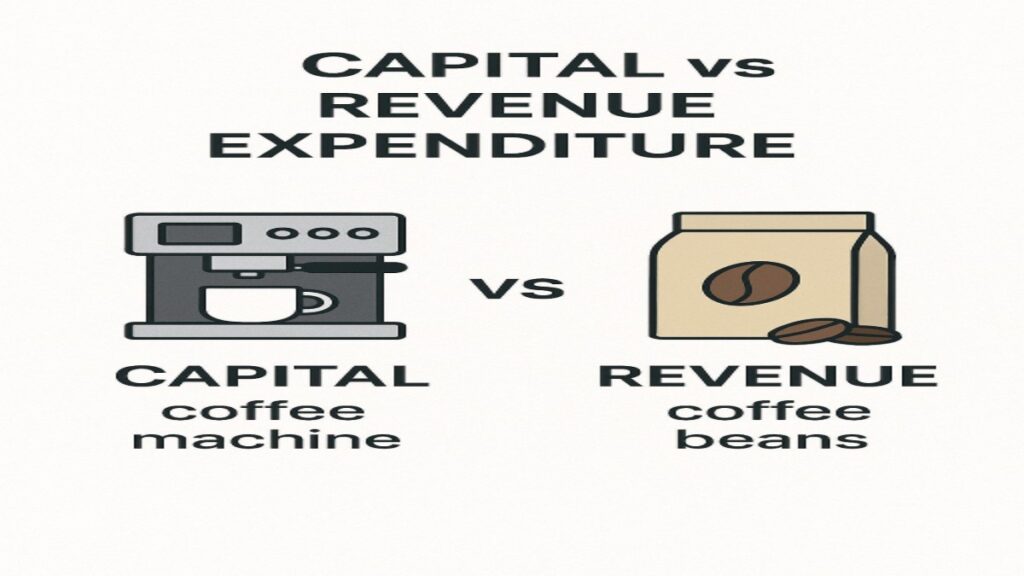
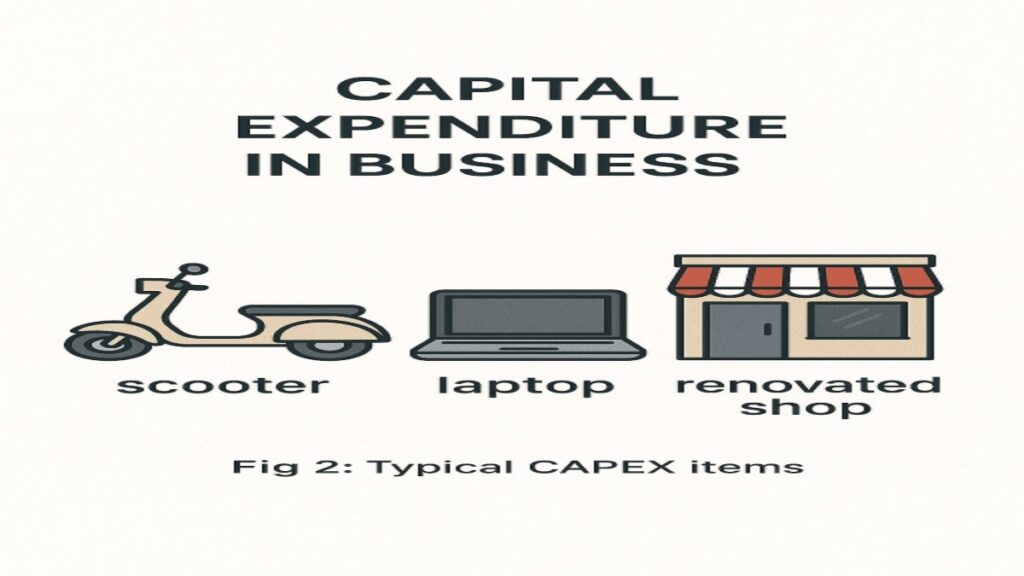
1. Capital Expenditure (CAPEX)
What it is:
Money spent to buy or upgrade assets used for years.
Examples:
| Item | Why CAPEX? |
|---|---|
| Delivery Scooter | Used for 5+ years |
| Laptop for billing | Lasts 3-4 years |
| Shop Renovation | Benefits long-term |
Accounting Magic:
- Appears in Balance Sheet (as asset)
- Depreciated yearly (value reduced gradually)
💡 Student Tip:
Think: “Is this a long-term friend?” → If yes, CAPEX!
2. Revenue Expenditure (OPEX)
What it is:
Money spent for daily operations to earn income now.
Examples:
| Item | Why OPEX? |
|---|---|
| Coffee Beans | Used up immediately |
| Monthly Rent | Recurring cost |
| Staff Salaries | Paid every month |
Accounting Magic:
- Appears in Profit & Loss Account
- Fully deducted in same year
💡 Student Tip:
Think: “Is this a daily need?” → If yes, OPEX!

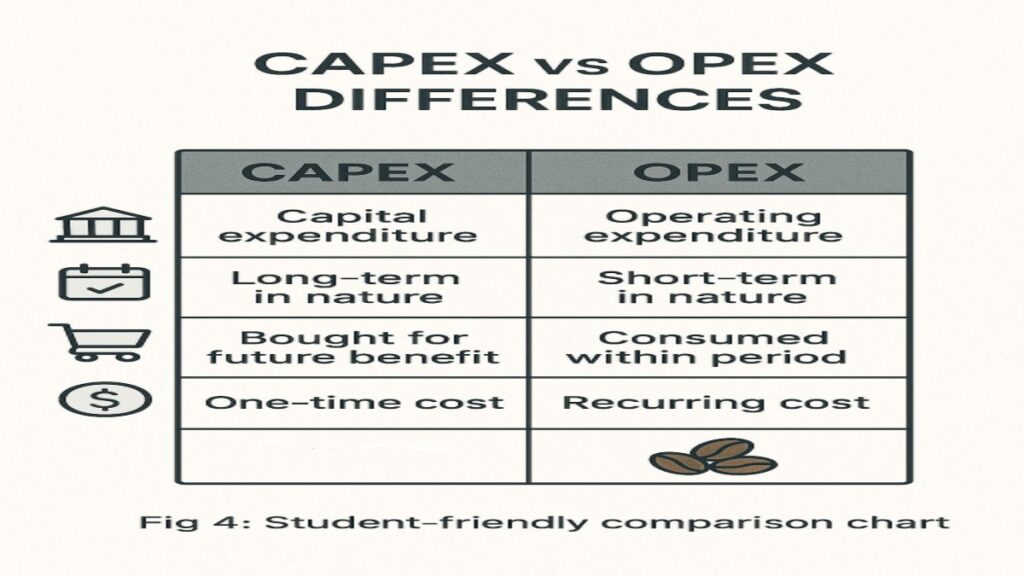
Key Differences: CAPEX vs OPEX Cheat Sheet
| Test | Capital Expenditure | Revenue Expenditure |
|---|---|---|
| Time | Benefits >1 year | Benefits ≤1 year |
| Value | Usually high (₹10k+) | Usually low (daily costs) |
| Frequency | One-time purchase | Recurring expense |
| Where Recorded | Balance Sheet | Profit & Loss Account |
| Tax Benefit | Claim depreciation yearly | Deduct fully in same year |
Image 4: Comparison Chart
Real-Life Cases (For Exams!)
Case 1: Computer Purchase
- ₹40,000 laptop for business → CAPEX
(Balance Sheet Asset → Depreciated over 4 years)
Case 2: Printer Repair
- ₹2,000 to fix paper jam → OPEX
(Full expense in P&L this year)
Case 3: Software Upgrade
- ₹15,000 for new features →
- If extends software life → CAPEX
- If routine update → OPEX
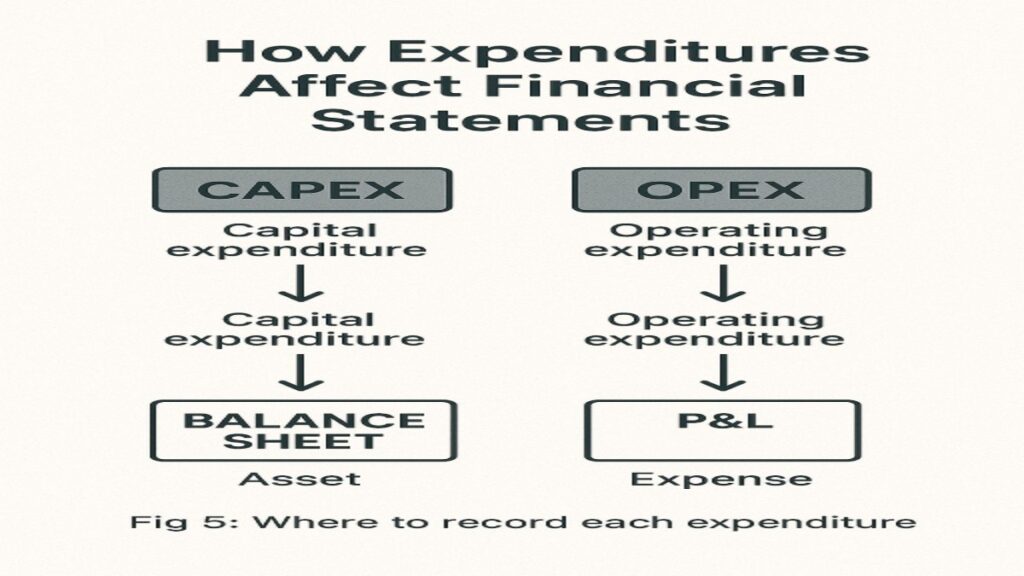
Accounting Entries Simplified
CAPEX Entry
Rohan buys ₹5 Lakhs coffee machine:
text
Copy
Download
Coffee Machine A/c Dr. 5,00,000
To Bank A/c 5,00,000
(Appears in Balance Sheet as Asset)
OPEX Entry
Rohan pays ₹20,000 electricity bill:
text
Copy
Download
Electricity A/c Dr. 20,000
To Bank A/c 20,000
(Appears in P&L Account as Expense)
Image 5: Accounting Impact
Test Yourself! (Answers Below)
- ₹50,000 for AC in office → ❓
- ₹10,000 monthly internet bill → ❓
- ₹2 Lakhs for trademark → ❓
- ₹5,000 for printer ink → ❓
- ₹7 Lakhs delivery van → ❓
Answers:
- CAPEX (Long-term use)
- OPEX (Recurring cost)
- CAPEX (Intangible asset)
- OPEX (Daily consumable)
- CAPEX (Lasts years)
Why This Matters?
- Exams: 30% of accounting questions
- Business: Impacts profit calculation
- Taxes: Wrong classification = penalties!
💼 Real Impact:
Treating ₹5 Lakhs machine as OPEX → Profit understated by ₹5 Lakhs!
3 Golden Rules for Exams
- Duration Test:Benefit >1 year? → CAPEX
- Recurrence Test:Monthly payment? → OPEX
- Value Test:Big amount? → Usually CAPEX
Conclusion
Master CAPEX vs OPEX to:
- Score 90%+ in exams 📚
- Avoid accounting mistakes 💼
- Understand business finances 🚀
Start Today: Classify your monthly expenses as CAPEX/OPEX
