(Perfect for FYBCom, BBA, and Accounting Students)
What are Final Accounts? Think Report Card 📝
Imagine your business is like your college semester:
- Trading Account = Your subject-wise marks
- P&L Account = Your final CGPA
- Balance Sheet = Your overall academic status
Final Accounts = Financial Report Card showing yearly performance!
✅ Why Adjustments?
Like correcting exam answers – we add forgotten items (unpaid rent, unsold stock) to show true results!
Image 1: Final Accounts Flow
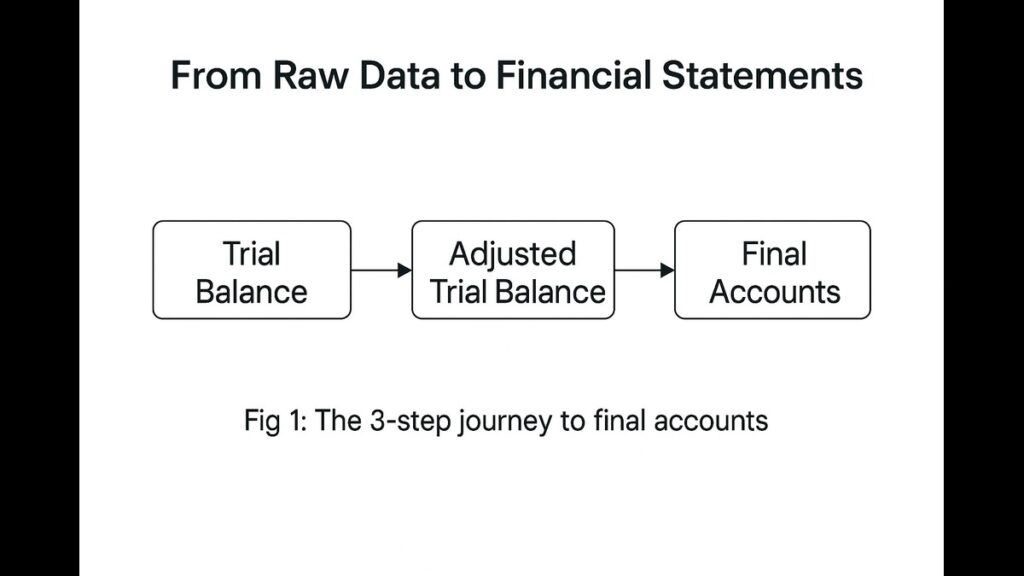
Step 1: Trading Account (Your “Gross Profit Calculator”)
What it does:
Calculates profit from buying and selling goods.
Simple Formula:
text
Copy
Download
Gross Profit = Sales - Cost of Goods Sold
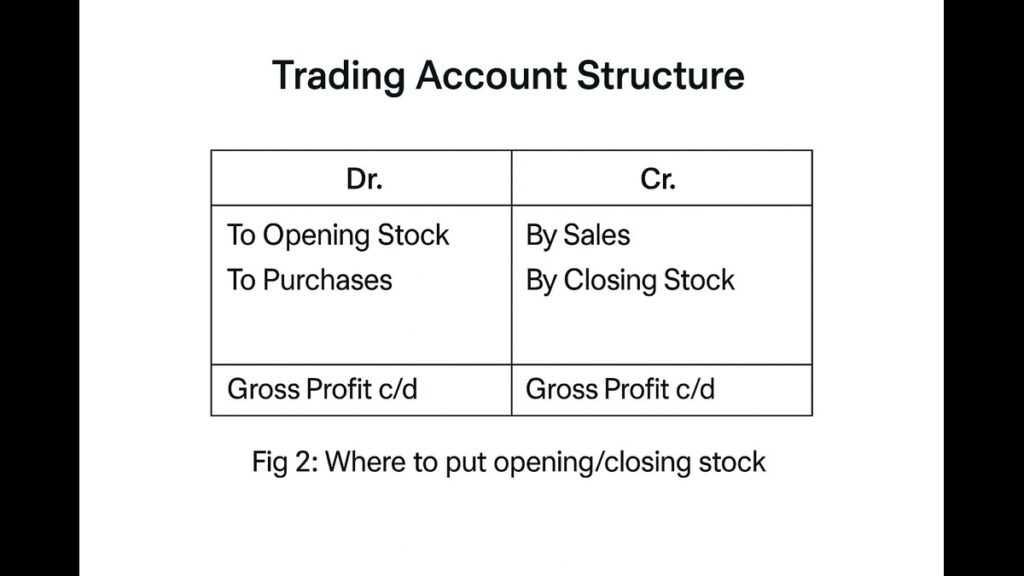
What goes inside?
| Debit Side (Costs) | Credit Side (Income) |
|---|---|
| • Opening Stock | • Sales |
| • Purchases | • Closing Stock (Adjustment!) |
| • Direct Expenses |
Key Adjustment:
- Closing Stock: Value of unsold goods → Add to credit side
💡 Example:
Bought goods ₹50,000, Sold for ₹80,000, Unsold stock ₹10,000
Gross Profit = 80,000 – (50,000 – 10,000) = ₹40,000
Image 2: Trading Account Format
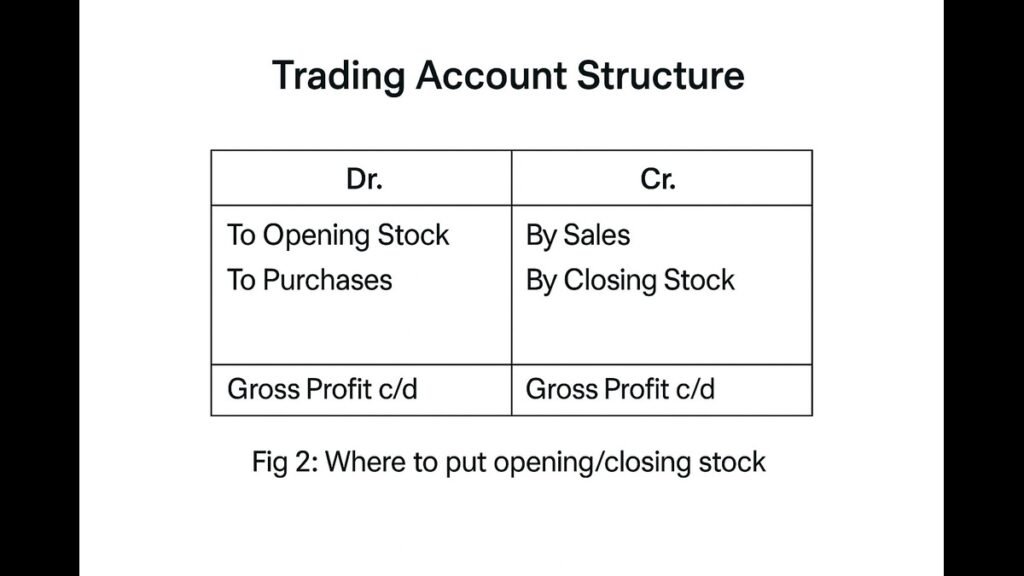
Step 2: Profit & Loss Account (Your “Net Profit Finder”)
What it does:
Calculates final profit after all expenses.
Simple Formula:
text
Copy
Download
Net Profit = Gross Profit + Other Income - All Expenses
Common Adjustments:
| Adjustment | Where to Put |
|---|---|
| Outstanding Rent | Add to Expenses |
| Prepaid Insurance | Reduce Expenses |
| Depreciation | Add to Expenses |
| Bad Debts | Add to Expenses |
Image 3: P&L Account Format
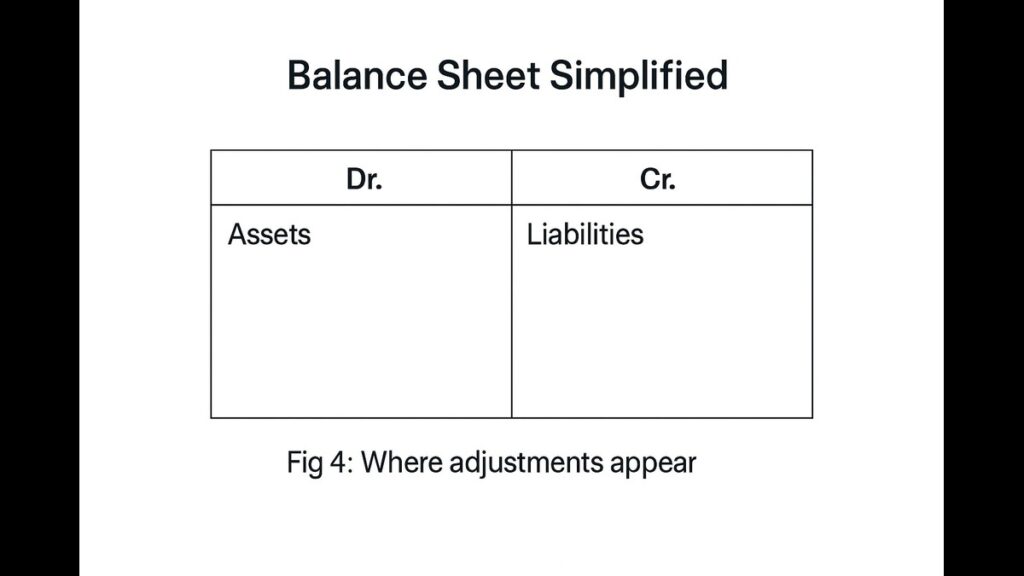
Step 3: Balance Sheet (Your “Financial Selfie” 📸)
What it shows:
- What you OWN (Assets)
- What you OWE (Liabilities)
- Your NET WORTH (Capital)
Adjustment Impact:
| Adjustment | Balance Sheet Effect |
|---|---|
| Closing Stock | Asset ↑ |
| Outstanding Rent | Liability ↑ |
| Prepaid Insurance | Asset ↑ |
| Depreciation | Asset ↓ |
Image 4: Balance Sheet Format
5 Must-Know Adjustments (With Examples)
- Closing Stock (₹20,000 not recorded)textCopyDownloadClosing Stock A/c Dr. 20,000 To Trading A/c 20,000 → Adds to Trading Cr. & Balance Sheet Asset
- Outstanding Salary (₹15,000)textCopyDownloadSalary A/c Dr. 15,000 To Outstanding Salary A/c 15,000 → Adds to P&L Expense & Liability
- Depreciation (10% on ₹1,00,000 Machinery)textCopyDownloadDepreciation A/c Dr. 10,000 To Machinery A/c 10,000 → Adds to P&L Expense & Reduces Asset Value
- Prepaid Rent (₹5,000)textCopyDownloadPrepaid Rent A/c Dr. 5,000 To Rent A/c 5,000 → Reduces Rent Expense & Becomes Asset
- Bad Debts (Customer won’t pay ₹8,000)textCopyDownloadBad Debts A/c Dr. 8,000 To Debtors A/c 8,000 → Adds to P&L Expense & Reduces Debtors
Pizza Shop Example 🍕
Trial Balance:
- Sales: ₹3,00,000
- Purchases: ₹1,80,000
- Rent: ₹24,000
Adjustments:
- Closing Stock: ₹40,000
- Rent Prepaid: ₹4,000
- Equipment Depreciation: ₹10,000
Solution:
Trading Account:
| Expenses | ₹ | Income | ₹ |
|---|---|---|---|
| Purchases | 1,80,000 | Sales | 3,00,000 |
| Gross Profit c/d | 1,60,000 | Closing Stock | 40,000 |
| Total | 3,40,000 | Total | 3,40,000 |
P&L Account:
| Expenses | ₹ |
|---|---|
| Rent (24k-4k) | 20,000 |
| Depreciation | 10,000 |
| Net Profit | 1,30,000 |
Balance Sheet:
| Assets | ₹ | Liabilities | ₹ |
|---|---|---|---|
| Closing Stock | 40,000 | Capital | XXXX |
| Prepaid Rent | 4,000 | Add: Net Profit | 1,30,000 |
| Equipment (Net) | 90,000 |
Image 5: Adjustment Impact
3 Golden Rules for Exams ✨
- Closing Stock:
- Trading Account (Credit side)
- Balance Sheet (Asset)
- Prepaid Expenses:
- Deduct from expense in P&L
- Show as Asset in Balance Sheet
- Depreciation:
- Add to P&L Expenses
- Deduct from Asset value
💡 Pro Tip:
Create a checklist:
“Did I remember Closing Stock? Outstanding Expenses? Depreciation?”
Why This Matters?
- 50% of your accounting exam marks
- Used by real businesses every month
- Foundation for CA/CMA/CS courses
Conclusion
Master final accounts with adjustments to:
- Score 90%+ in exams 📚
- Understand business finances 💼
- Build a great career in finance 🚀
Start Today: Solve 1 adjustment problem daily!
