
📘 Why Learn Basic Accounting Terms?
If you’re new to commerce or preparing for exams like UGC NET/SET, M.Com entrance, or MBA, learning the language of accounting is your first step.
Accounting is not just about numbers—it’s about understanding how a business speaks. And that language is built on these core terms.
Knowing these terms will help you:
- ✅ Solve numerical problems correctly
- ✅ Understand journal entries, ledgers, and balance sheets
- ✅ Write perfect theory answers in exams
- ✅ Crack MCQs in NET/SET or PGD entrance
🔑 12 Must-Know Accounting Terms (With Examples)
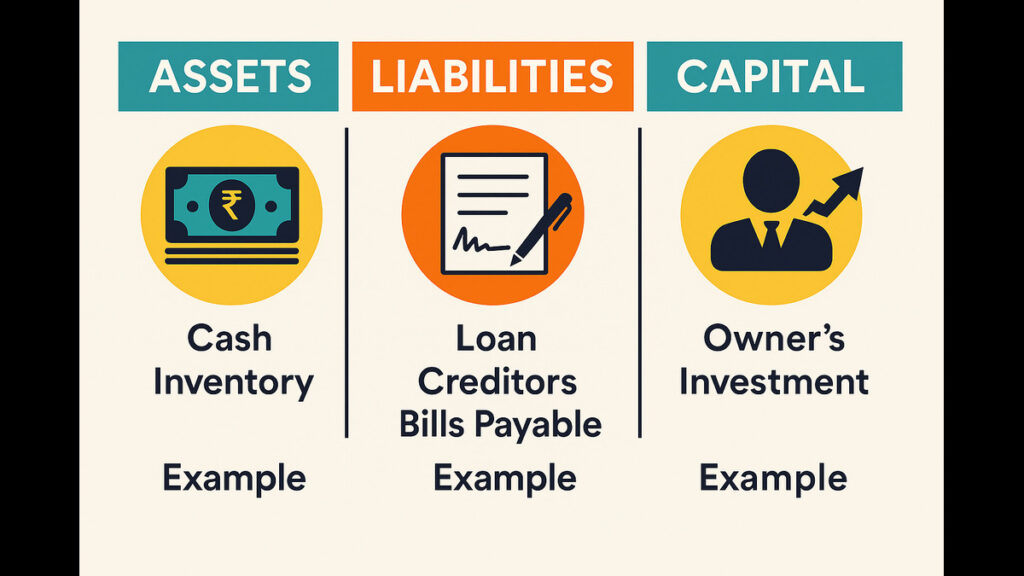
1. Assets
Assets are things owned by a business that have value.
📌 Example: Cash, Furniture, Building, Inventory, Computers.
These help the business earn money.
💡 Real Life: A shopkeeper’s counter, cash register, and stock are all assets.
2. Liabilities
Liabilities are things the business owes to others.
📌 Example: Bank loan, Creditors, Bills Payable, Outstanding Rent.
💡 Tip: If you have to pay someone in the future, that’s a liability.
3. Capital
Capital is the amount invested by the owner in the business.
📌 Example: Owner brings ₹1,00,000 to start the business.
💡 It increases when there’s a profit, decreases with loss or drawings.
4. Revenue (Income)
Revenue is the income earned by the business through its main operations.
📌 Example: Sales of goods, Fees received, Interest income.
💡 Net Profit = Revenue – Expenses
5. Expenses
Expenses are the costs incurred to run the business.
📌 Example: Salary, Rent, Electricity, Telephone bills.
💡 These reduce the profit and are recorded in the Profit & Loss Account.
6. Drawings
Drawings are withdrawals made by the owner for personal use from the business.
📌 Example: Owner takes ₹5,000 cash or goods worth ₹2,000.
💡 Drawings reduce Capital.
7. Debtors
Debtors are people who owe money to the business.
📌 Example: You sold goods worth ₹10,000 on credit → That customer is a debtor.
💡 They are assets, as they bring money in the future.
8. Creditors
Creditors are people to whom the business owes money.
📌 Example: You bought goods worth ₹15,000 on credit from a supplier → They are your creditors.
💡 Creditors are liabilities.
9. Journal
The Journal is the book where transactions are recorded in date order.
📌 Every entry has debit and credit sides.
💡 Also called “Book of Prime Entry” or “Day Book.”

10. Ledger
The Ledger is the book where all journal entries are grouped account-wise.
📌 Example: All entries related to Cash go into the Cash Ledger, all Sales into Sales Ledger.
💡 It helps in making the Trial Balance.
11. Trial Balance
The Trial Balance is a list of all ledger balances (debit and credit) to check mathematical accuracy.
📌 If both sides match → entries are correct.
💡 Used to prepare final accounts.
12. Final Accounts
These are the reports made at the end of the year to know the financial status.
They include:
- Trading Account
- Profit & Loss Account
- Balance Sheet
💡 Used by owner, banks, investors to check business health.

🎯 Bonus Tip for Students:
These terms are commonly seen in:
- FYBCom Unit 1 & 2 theory papers
- M.Com and MBA entrance exams
- UGC NET/SET Paper 2 – Commerce
- Practical case studies
Prepare flashcards with these terms. Use them in journal problems. Understand, don’t memorize.
🧾 Final Summary
| Term | Meaning | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Assets | What business owns | Cash, Stock, Furniture |
| Liabilities | What business owes | Bank Loan, Creditors |
| Capital | Owner’s investment | ₹1,00,000 invested |
| Income | Revenue earned | Sales, Interest Received |
| Expenses | Costs to run business | Rent, Salary |
| Drawings | Owner’s withdrawals | ₹5,000 cash taken |
