Introduction
In today’s interconnected global economy, understanding international taxation has become essential for commerce and finance students. Whether you’re pursuing B.Com, M.Com (International Taxation), MBA, or preparing for UGC NET/SET in Commerce, this guide provides a student-friendly explanation of key international tax concepts, laws, and real-world applications.
Table of Contents
- What is International Taxation?
- Key Concepts: Residence vs. Source Rule
- Understanding Double Taxation (and How to Avoid It)
- The Role of Tax Treaties (DTAAs)
- Introduction to Transfer Pricing
- Why Should Students Learn International Taxation?
- Practical Example: DTAA in Action
1. What is International Taxation?
International taxation refers to how different countries apply tax rules to cross-border transactions involving individuals, companies, and organizations. It answers questions such as:
- Who pays tax on international income?
- Which country gets the tax?
- How to prevent double taxation?
📋 Key Terms for Students: Cross-border income, tax liability, source jurisdiction, tax residence

2. Key Concepts: Residence vs. Source Rule
Countries use two main rules for taxation:
- Residence Rule: A country taxes its residents on their worldwide income.
- Source Rule: A country taxes only the income generated within its borders.
🎓 Quick Tip: Learn how different countries (like India, USA, UK) apply these rules in exams.
3. Understanding Double Taxation
Double taxation happens when the same income is taxed twice:
- Once in the country where income is earned (source country)
- Again in the country where the taxpayer resides
Solutions to Avoid Double Taxation:
- Tax Credit System
- Tax Exemption System
- Double Taxation Avoidance Agreements (DTAAs)
📋 Exam Focus: DTAAs are frequently asked in B.Com/M.Com and UGC NET Paper 2 Commerce.

4. The Role of Tax Treaties (DTAAs)
DTAAs (Double Taxation Avoidance Agreements) are signed between countries to prevent unfair taxation. They:
- Clarify which country taxes what type of income
- Lower withholding tax rates
- Promote global investment
📖 For Students: Study the India-USA DTAA or India-Mauritius DTAA to understand how tax savings happen in real life.

5. Introduction to Transfer Pricing
Transfer pricing refers to the pricing of goods/services between associated enterprises in different countries (like a parent company and its foreign subsidiary).
Why It Matters:
- Prevents profit shifting to low-tax countries
- Ensures fair taxation of multinational companies
📋 For MBA & M.Com: Important topic in international business taxation modules.
6. Why Should Students Learn International Taxation?
- Career Boost: Taxation is a core subject in CA, CS, CMA, and finance-related exams
- Job Opportunities: High demand for international tax experts in MNCs, Big 4 firms, and government
- Competitive Exams: Topics on DTAAs and global tax rules are now part of UGC NET Commerce and SET exams
- Global Awareness: Understand how countries manage cross-border e-commerce, freelancing income, and crypto taxation
📋 Career Tip: Add “Knowledge of International Taxation” on your LinkedIn and resume to stand out.

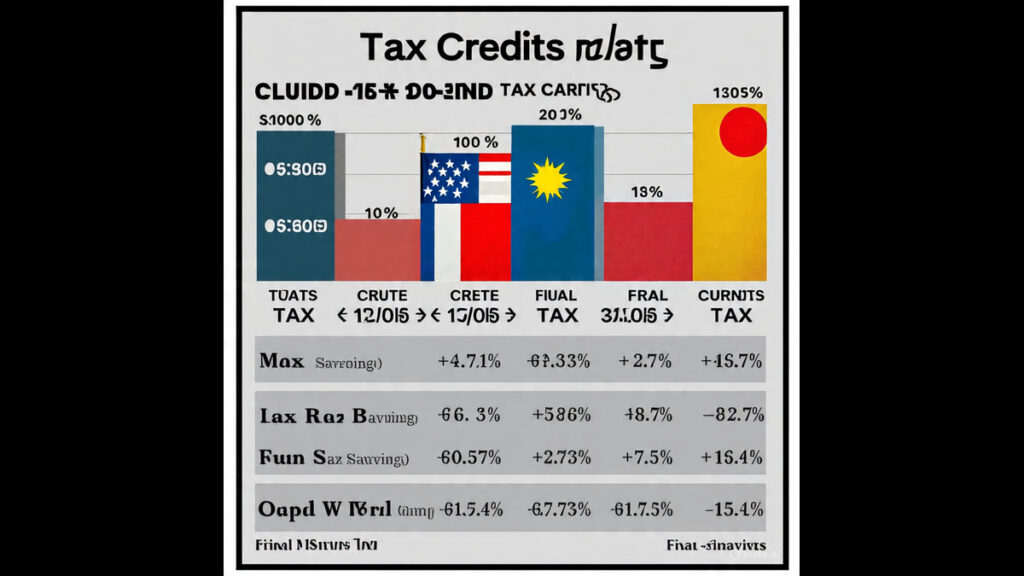
7. Practical Example: DTAA in Action
Case:
An Indian freelancer earns $10,000 from US clients.
- USA (Source Country): Withholds 10% tax = $1,000
- India (Residence Country): Taxes 30% on global income = $3,000
Thanks to DTAA: India allows a tax credit of $1,000.
So, freelancer pays only $2,000 more in India (not full $3,000).
📋 Learnings: This case is useful for answering real-world application questions in case study-based exams.
Conclusion
Mastering international taxation is no longer optional for commerce students—it’s a necessity. From scoring high in university exams to building a global career, knowledge of residence-based taxation, DTAAs, and transfer pricing opens many doors.
Stay updated with tax laws. Practice MCQs. Read real DTAA agreements. And when your YouTube video is ready, add it here to enhance your understanding!
✅ Subscribe to our blog & YouTube channel for more practical guides on Commerce, Taxation & NET exam prep!
Image/Video Credits
All graphics from Pexels, Unsplash, or custom-created by Commerce Edu Hub.
